As a viola player, you know that the quality of your strings directly impacts your instrument's sound and playability. Over time, strings wear out and need to be replaced to maintain optimal performance. Learning how to replace your viola strings independently is a valuable skill that can save you time and money overall. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the process of replacing your viola strings, discuss the distinct types of strings available and their pros and cons, and highlight the parts of the viola involved in string replacement.
Understanding Viola String Types and Their Advantage
Before diving into the string replacement process, it is essential to understand the several types of viola strings available and their unique characteristics. The three most common materials used for viola strings are gut, synthetic core, and steel core.
- Gut strings: Made from sheep intestines, gut strings are known for their warm, rich tone. They offer a traditional sound that many players prefer. However, they are sensitive to humidity and temperature changes, requiring more frequent tuning.
- Synthetic core strings: These strings have a synthetic core, such as nylon or Perlon, wrapped with metal. They offer a balanced tone that blends warmth and brightness, making them a popular choice for many violists. Synthetic core strings are more stable than gut strings and less prone to tuning issues.
- Steel core strings: With a solid steel core wrapped with metal, these strings produce a bright, powerful sound. They are the most durable and stable option, making them ideal for players who perform frequently or in demanding environments. However, some players find their tone too harsh or lacking in warmth compared to other string types.
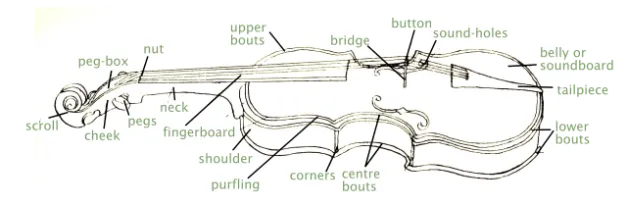
Identifying Viola Parts for String Replacement
To replace your viola strings successfully, you will need to familiarize yourself with the relevant parts of your instrument. These include:
- Tailpiece: The anchoring point for the strings at the bottom of the viola.
- Fine tuners: Small metal screws attached to the tailpiece that allow for minor tuning adjustments.
- Bridge: The wooden piece that supports the strings and transfers their vibrations to the body of the viola.
- Nut: The small, grooved piece at the top of the fingerboard where the strings rest.
- Pegs: The wooden pieces at the top of the viola used for larger tuning adjustments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing Viola Strings
Now that you understand the types of strings and the parts of your viola involved in string replacement, let’s walk through the process step by step.
Step 1: Gather your tools and supplies
You will need the following items:
– New set of viola strings
– String winder (optional but recommended)
– Pencil
– Soft cloth
– Fine-toothed comb (optional)
Step 2: Remove the old strings
- Loosen the old strings by turning the pegs until there is slack.
- Carefully remove the strings from the tailpiece and the pegs.
- Use a soft cloth to clean the fingerboard, bridge, and body of the viola.
Step 3: Install the new strings
- Begin with the lowest string (C) and work your way up to the highest (A).
- Thread the string through the hole in the tailpiece and insert the ball end into the fine tuner (if applicable).
- Insert the other end of the string into the hole in the peg, leaving a bit of slack.
- Wind the string around the peg, ensuring that each wind is slightly below the previous one and that the string wraps towards the inside of the peg box.
- Gently pull the string taut and turn the peg to tighten it until the string is in tune.
- Repeat this process for the remaining strings.
Step 4: Tune and stretch the new strings
- Use a tuner to bring each string up to its proper pitch gradually.
- Gently stretch each string by pulling it away from the fingerboard and releasing it. This helps prevent the strings from slipping out of tune too quickly.
- Retune the strings as needed, as they may stretch and go flat during this process
Step 5: Final adjustments and cleanup
- Once the strings are fully stretched and in tune, use a pencil to lubricate the grooves in the nut and bridge to prevent string binding.
- If needed, use a fine-toothed comb to smooth out any stray string fibers at the end of the fingerboard.
- Play each string to ensure they are properly seated and vibrating clearly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues During String Replacement
While replacing viola strings is straightforward, you may encounter some common issues. Here are a few tips to help you troubleshoot:
- String slippage: If a string keeps slipping out of tune, ensure that it is wound correctly around the peg and that there is enough tension. You can also apply a small amount of peg compound to help the peg grip the string.
- Buzzing or rattling sounds: If you hear buzzing or rattling after replacing strings, check that the strings are seated properly in the nut and bridge grooves. Ensure that the bridge is standing upright and not leaning forward or backward.
- Difficulty tuning: If you find it challenging to tune the new strings, give them time to stretch and settle. Tune them gradually, and do not be discouraged if they require frequent retuning in the first few days.

Conclusion
Replacing your viola strings is an essential maintenance task that every violist should learn. By understanding the different string types, their advantages, and the parts of your instrument involved in string replacement, you can confidently tackle this process and keep your viola sounding its best. Regular string replacement will not only improve your instrument’s sound and playability but also prolong its life.
To further enhance your knowledge of viola maintenance and playing techniques, consider exploring the comprehensive online music education resources offered by Practicing Musician. Their video tutorials and lessons cover a wide range of topics, making them a valuable resource for violists of all skill levels.
Check out this informative video from Practicing Musician to learn more about the parts of your viola and viola bow maintenance:
Getting To Know Your Viola: Parts Of Your Viola
Cleaning Your Viola








Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.